More and more Ukrainians are thinking about how to optimize their utility costs and make their home or apartment as comfortable as possible. One of the key solutions in this direction is DIY heating. This not only helps save money but also allows you to fully control the heating process, choose the right type of system and materials. In this article, we will look at the main types of heating systems that can be installed by yourself (water, air, steam), and we will also give tips on how to make heating in a house, apartment, or greenhouse without unnecessary expenses.
Useful videos on the topic
1. Why you should do heating yourself
-
Cost savings
- The cost of installation by professional craftsmen can be quite high.
- By installing the system yourself, you only pay for materials and equipment, while doing the work yourself.
-
Quality control
- You choose proven materials that suit you in terms of price and technical characteristics.
- You know every stage of the installation, so in case of malfunctions, you can quickly find and fix the problem.
-
Flexibility in choosing solutions
- You can combine different energy sources: gas, solid fuel, electricity, solar collectors, etc.
- It is easier to make changes to the project, adapting it to the specific needs of the house, apartment, or greenhouse.
2. Main types of heating that can be done independently
2.1 Water heating for the house by yourself
Water heating is one of the most popular and effective ways to heat a private house. Its principle lies in the circulation of hot water (heat carrier) through a system of pipes and radiators.
-
Advantages
- Even distribution of heat throughout the house.
- You can use different boilers (gas, solid fuel, electric).
- High energy efficiency if installed and insulated correctly.
-
Disadvantages
- Installation of the system requires strict adherence to technologies (calculating pipe diameters, choosing a pump, etc.).
- In case of serious mistakes, leaks and pipe bursts may occur.
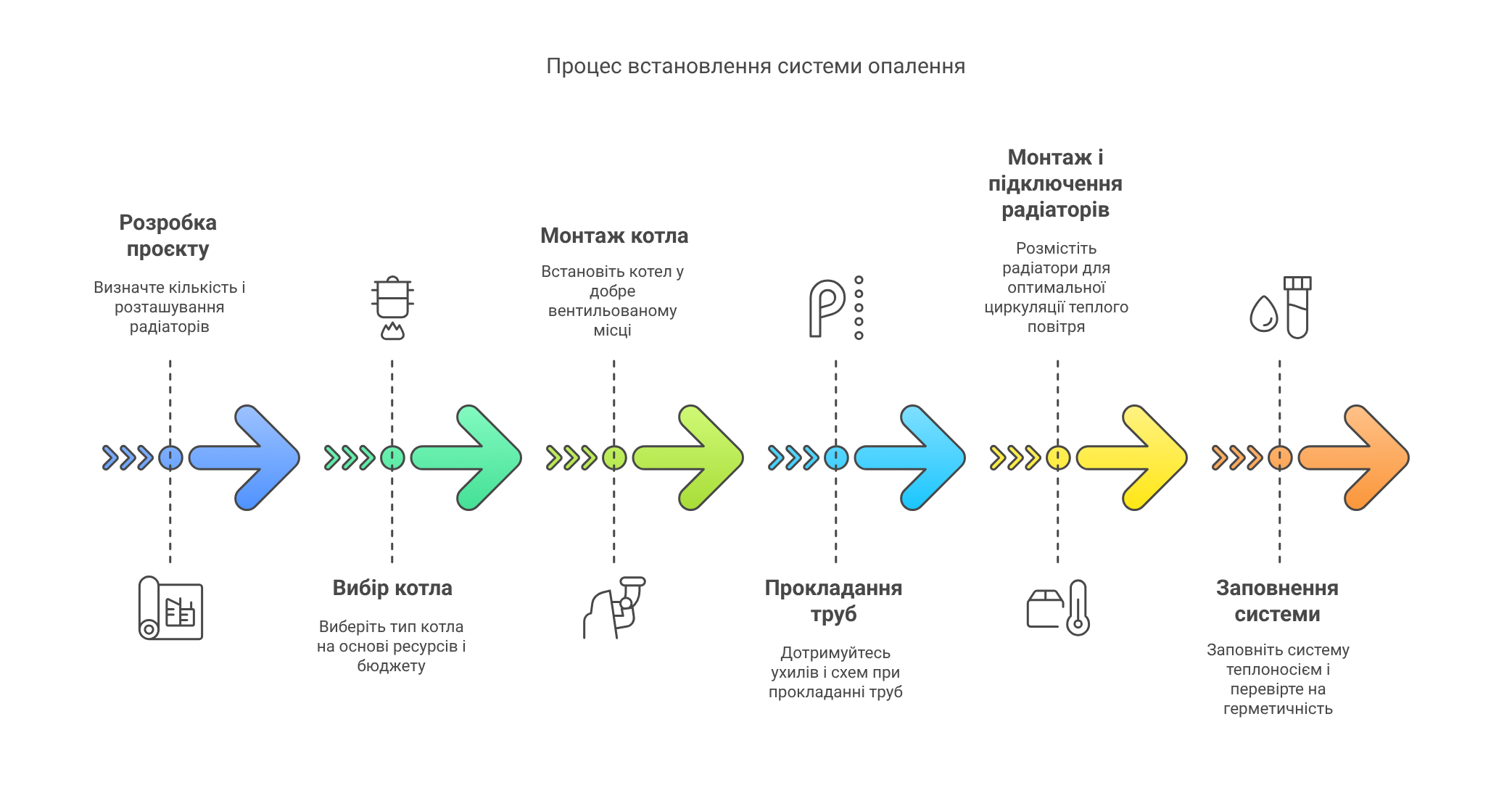
Main stages of installing water heating
- Project development: determine the number of radiators, their location, length, and diameter of pipes.
- Choosing a boiler: gas, solid fuel, or electric – depending on the availability of resources and budget.
- Boiler installation: install the boiler in a place with good ventilation (especially for gas or solid fuel boilers).
- Laying pipes: follow slopes and recommended schemes (single-pipe or two-pipe system, “warm floor,” etc.).
- Installation and connection of radiators: place them mainly under windows or near external walls for better circulation of warm air.
- Filling the system with heat carrier and checking for tightness (hydraulic test).
2.2 Air heating by yourself
Air heating uses heated air that is distributed throughout the house using fans and air ducts.
-
Advantages
- Quick heating of the room.
- Ability to combine with ventilation and air conditioning.
- No radiators and pipes, simplifying interior design.
-
Disadvantages
- More complex design of the air duct system that needs to be carefully calculated.
- Higher likelihood of air drying out.
- Filters need to be installed for air purification.
How to make air heating
- Heating source: usually, a gas or electric heating chamber is used.
- Installation of air ducts: pipes made of metal or special non-combustible materials that distribute warm air throughout the rooms.
- Installing a fan: ensures circulation of warm air.
- Insulation: be sure to insulate the air ducts to avoid heat loss.
- Cold air intake system: organize the return of cooled air to the heater for reheating (recuperation).
2.3 Steam heating by yourself
Although steam heating is used less frequently today, it remains relevant for industrial facilities and some private homes. The principle is that steam is generated in the boiler, which then moves through pipes to the radiators.
-
Advantages
- Quick heating of radiators and rooms.
- High temperature of the heat carrier can be effective in severe frosts.
-
Disadvantages
- High requirements for the quality of pipes and connections (high temperature and pressure).
- Higher risk of burns, as the surface of radiators and pipes becomes very hot.
- More complex installation and stricter safety requirements.
3. How to choose a boiler for heating
- Heating area: calculate the thermal power of the boiler based on the standard of 1 kW per 10 m² (but taking into account the insulation of the house).
- Type of fuel: availability of gas, possibility of storing firewood or pellets, availability of a powerful electrical network.
- Cost and maintenance: consider the initial price of the boiler, the cost of fuel, and regular service.
- Energy efficiency and environmental friendliness: modern boilers have special technologies that reduce fuel consumption and harmful emissions.
Popular types of boilers
- Gas: high efficiency, relative cheapness of gas, but require connection to the gas pipeline and compliance with many standards.
- Solid fuel: versatile (firewood, coal, pellets), but require more time for maintenance, fuel loading, and cleaning.
- Electric: easy to install, safe, but electricity bills can be quite high.
4. Installation of radiators and pipes in a water or steam heating system
-
Radiators
- Choose based on heat output and material (aluminum, bimetal, cast iron).
- Install under windows or near external walls.
- Be sure to use thermostats to accurately set the temperature.
-
Pipes
- Choose quality materials: metal-plastic, polypropylene, or copper (depending on budget and operating conditions).
- Follow slopes for natural circulation or install a pump for forced circulation.
- Before starting the system, conduct a hydraulic test (increased pressure) to detect possible leaks.
5. How to make heating in an apartment
In an apartment, the possibilities for installing an autonomous heating system are limited due to legislative requirements and technical conditions. However, there are options:
-
Electric heating
- The simplest way is to use electric convectors or infrared panels.
- Does not require laying pipes and installing a gas boiler.
- It is important to calculate the power to avoid overloading the network.
-
Gas heating (two-circuit boiler)
- Suitable if there is gas in the house and individual heating installation is allowed.
- Requires obtaining permits (from the gas service, from the housing office, etc.) and careful installation in compliance with safety standards.
-
“Warm floor” system
- Can be electric (film, cable) or water (if there is a possibility of connection).
- Creates even heat, but requires careful insulation of the floor and can be complex to install, especially in multi-apartment buildings.
6. How to make heating in a greenhouse (especially in a metal one)
A greenhouse, especially a metal one, requires a special approach to heating, as heat loss can be significantly greater than in a living space.
-
Insulating the frame and walls
- Use modern materials (polycarbonate instead of film) that retain heat well.
- Sealing doors and windows will help reduce heat loss.
-
Types of heating for a greenhouse
- Air: install a small heat fan or air duct from the main heat source (if the greenhouse is located close to the house).
- Water: lay pipes with hot water in the ground. Possible connection to the house system or a separate low-power boiler.
- Electric: infrared heaters or “warm floor” cable under the ground.
- Solid fuel stove: a budget option, but requires regular addition of firewood or coal.
-
Metal greenhouse by yourself
- Frame: metal profile or pipe, covering – polycarbonate.
- Heating: if the greenhouse is small, it is convenient to use electric devices (infrared emitters). For larger areas, consider water heating with pipes laid in the ground or along the walls.
- Ventilation system: do not forget about ventilation – it is important for the health of plants and humidity regulation.
7. Useful tips and recommendations
-
Carefully insulate the house or greenhouse
- Quality insulation of walls, floors, roofs, and sealing of windows minimizes heat loss.
- It is better to spend money on quality insulation than to pay more for heating.
-
Combine different heat sources
- For example, install a gas boiler and additionally use solar collectors or a solid fuel boiler to reduce gas costs.
- This will increase the reliability of the system and help save.
-
Use automation and modern technologies
- Thermostats, programmable room thermostats, “smart” control systems – all of this will allow you to use energy efficiently.
- Timely maintenance of the boiler, cleaning of radiators.
-
Follow safety rules
- When installing a gas or solid fuel boiler, be sure to consult specialists to check the chimney, ventilation, and quality of installation.
- Avoid self-activity in matters that require a special license (for example, gas work).
8. Conclusion
DIY heating is a real opportunity to reduce utility costs and obtain a reliable and efficient heating system, fully adapted to your needs. Whether you are planning water heating for the house, interested in air heating by yourself, or looking for a way to make heating in an apartment or in a greenhouse, the key is a competent project, quality materials, and adherence to technical standards. Do not forget about safety: in particular, the installation and connection of gas boilers and the installation of electrical equipment are better entrusted to professionals with the appropriate permits.
Combine different types of heating, take care of insulation, apply modern technologies – and your home or greenhouse will always be warm with minimal costs!
