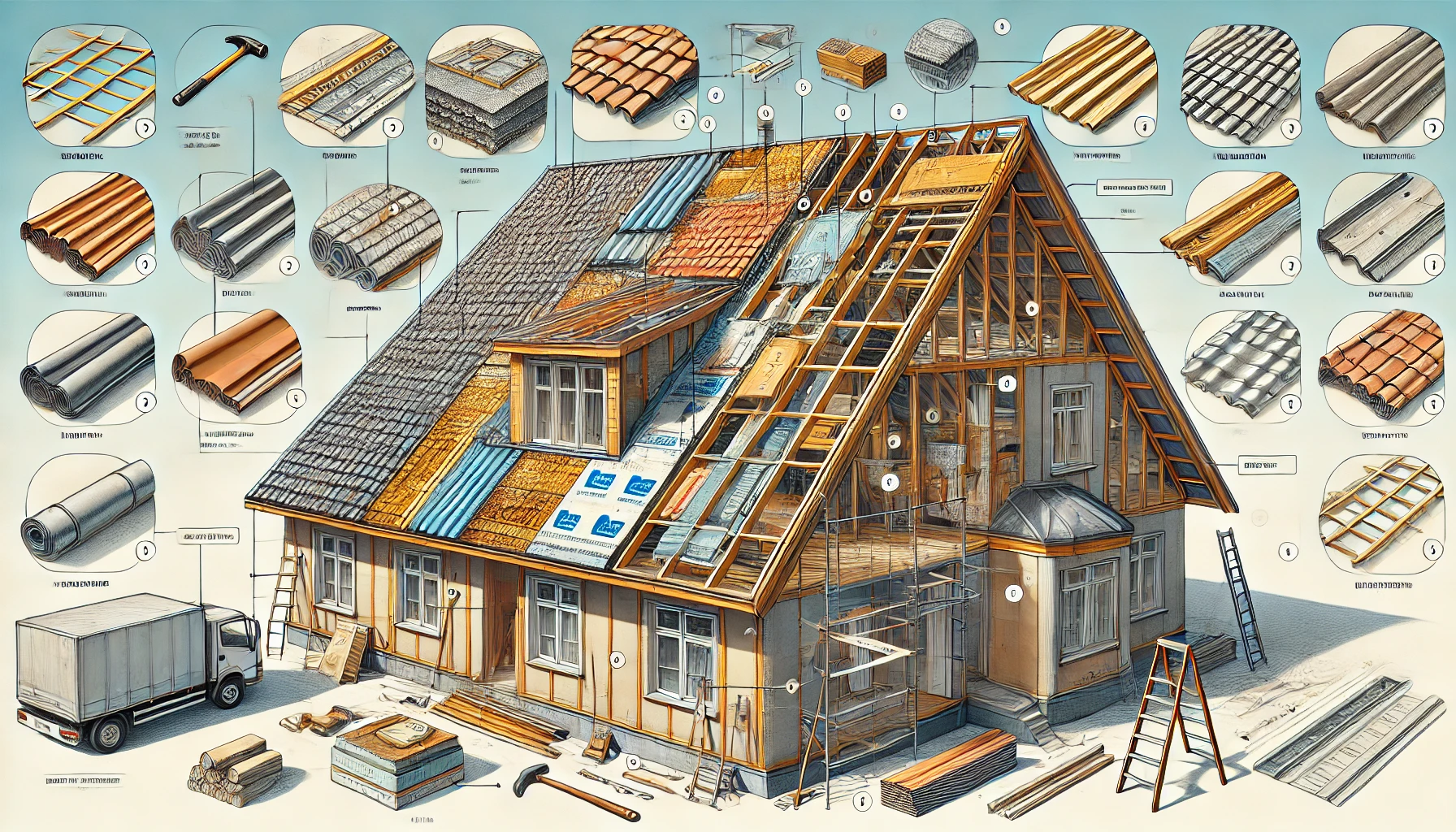
A gable roof (also known as a pitched roof) is one of the most common and affordable solutions for building residential houses. Its popularity is explained by the relative simplicity of the design, the efficiency of rainwater drainage, and reliable protection against adverse weather conditions. To ensure that the roof lasts for many years and provides comfort in the home, it is important to design it correctly, choose reliable roofing materials, and carry out the installation properly.
Useful videos on the topic
In this article, we will consider:
- The structure of a gable roof and its main elements.
- How to choose a roof project and determine the type of roofing.
- The main types of roofs and roofing materials.
- The stages of installation (including the battens, waterproofing, etc.).
- Tips for maintenance and preventive work.
- Answers to frequently asked questions (FAQ).
This comprehensive guide will help you better understand how to ensure an effective and durable roofing for a gable roof in your home.
1. The structure of a gable roof
1.1. Main elements
- Mauerlat. A beam or board that is fixed along the upper perimeter of the walls. It serves as a support for the rafters and evenly distributes the load from the roof onto the walls.
- Rafters. Sloped beams that form the “frame” of the roof. The strength of the entire structure depends on their quality and proper installation.
- Ridge beam. A horizontal element that connects the upper ends of the rafters and ensures the correct geometry of the roof.
- Roof battens. Cross boards or beams that are mounted on the rafters and serve as a base for attaching the roofing material. The battens can be solid or spaced, depending on the type of roofing.
- Roofing pie. Consists of:
- Waterproofing membrane (protects the insulation and rafters from moisture);
- Insulation (prevents heat loss in winter and excessive heating in summer);
- Vapor barrier (prevents moisture from entering the insulation from the room);
- Counter battens (provide a ventilation gap).
1.2. The principle of operation of a gable roof
Two slopes connected at an angle allow for quick and effective drainage of precipitation (rain, snow) from the structure. Thanks to the sloped shape, the load from wind and snow is distributed evenly, which contributes to the durability of the structure.
2. Types of roofs and features of gable structures
There are several types of roofs:
- Mono-pitched (have one slope).
- Gable (the most common in private residential construction).
- Hip roofs (for more complex projects).
- Broken (mansard) (allow for additional living space under the roof).
Among the listed options, gable roofs stand out:
- Ease of installation.
- Relatively simple design.
- Optimal material consumption.
- Good price-to-reliability ratio.
3. Designing a gable roof
3.1. Why a roof project is needed
A roof project is technical documentation that includes:
- Load calculations (snow, wind, the weight of the roofing).
- A scheme for the placement of rafters and additional supporting elements.
- Types and characteristics of roofing materials.
- Instructions for ventilation and thermal insulation of the roofing space.
Proper design helps avoid material overuse and problems with leaks or deformation of the roof in the future.
3.2. Choosing the slope angle
The slope angle of the slopes depends on:
- The climatic features of the region (heavy precipitation, strong winds).
- The type of roofing material (some materials require a minimum or maximum slope).
- Architectural requirements (the overall style of the house).
Typically, the slope angle for gable roofs ranges from 15 to 45 degrees.
4. Roofing materials for a gable roof
When choosing roofing, consider:
- Climate (amount of precipitation, temperature fluctuations).
- Budget (cost of the material and its installation).
- Desired appearance.
- Durability and noise level requirements (for example, metal tiles can be noisier during rain).
The most common types of roofing for gable roofs are:
-
Metal tiles
- Advantages: lightweight, quick installation, a wide range of colors, relatively affordable price.
- Disadvantages: increased noise level during rain, requires proper waterproofing and thermal insulation to avoid condensation.
-
Composite tiles
- Advantages: has an attractive appearance, better sound insulation than metal tiles.
- Disadvantages: more expensive than regular metal tiles.
-
Bitumen (flexible) tiles
- Advantages: excellent sound insulation, aesthetic design, ease of installation on complex areas.
- Disadvantages: requires solid battens and quality ventilation setup.
-
Onduline (euro slate)
- Advantages: lightweight, easy to install, resistant to corrosion.
- Disadvantages: lower durability, may lose color over time, lower resistance to mechanical damage.
-
Natural (ceramic) tiles
- Advantages: durability (up to 100 years), elegant appearance, eco-friendliness.
- Disadvantages: high cost, heavy weight (requires a reinforced rafter frame).
-
Slate
- Advantages: low cost, corrosion resistance, withstands snow weight.
- Disadvantages: brittle, may crack upon impact, less popular due to asbestos content (outdated standards).
-
Brick roofing
- This usually refers to roofing made of ceramic tiles or cladding the roof with special decorative elements. As an independent material, “brick” is not used for roofing, but decorative solutions are possible.
5. Stages of roof installation for a gable roof
5.1. Surface preparation and installation of the mauerlat
- Check the geometry of the upper part of the walls.
- Install the mauerlat (a wooden beam with a cross-section of 100×150 or 150×150 mm).
- Secure the mauerlat firmly to anchor bolts or chemical anchors, isolating the wood from direct contact with the stone (concrete) surface.
5.2. Installation of the rafter system
- Prepare and cut the rafters to the required length, considering the overhangs for the gable and eaves.
- Connect the rafters in pairs on the ground or on the upper floor (depending on complexity).
- Secure the rafters to the mauerlat with metal brackets and screws or nails.
- Check the symmetry of the two slopes.
5.3. Installation of waterproofing and battens
- Waterproofing film or membrane:
- Laid in horizontal rows with an overlap of 10–15 cm.
- Fixed with a construction stapler or special nails with wide heads.
- Counter battens:
- Fixed over the membrane along the rafters, creating a ventilation gap.
- Roof battens:
- Secured across the counter battens.
- The spacing of the battens depends on the chosen material (for example, for metal tiles — approximately 350 mm from center to center of the battens).
- For bitumen tiles, a solid battening is required (OSB boards or moisture-resistant plywood).
5.4. Installation of roofing material
- Start laying from the bottom row (eaves) towards the ridge.
- Check the parallelism of the rows relative to the eaves board.
- Carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions for each type of roofing (attachment method, required slope, recommended sealants, etc.).
5.5. Finishing works and drainage system
- Install ridge elements, end plates, snow guards (if necessary).
- Secure the gutters and downpipes.
- Check all joints for tightness.
6. Maintenance of a gable roof: tips and recommendations
-
Regular condition checks
– Inspect the roof twice a year: in spring and autumn.
– Identify damages (cracks, shifted sheets) and address them immediately. -
Cleaning from debris
– Remove leaves, branches, and other debris that may accumulate in the gutters or on the roof.
– Clogged gutters can lead to water stagnation and leaks. -
Sealing joints
– Check the condition of sealants, gaskets, ridge connections.
– Update insulating and sealing materials in a timely manner. -
Replacing damaged elements
– If cracks or holes are found in the roofing material, replace individual sheets or tiles. -
Checking the condition of the wood
– Inspect the rafters and battens for mold or mildew. Treat the wood with antiseptics if necessary.
Regular maintenance of the roof will significantly extend its service life and protect the house from leaks and heat loss.
FAQ
1. What are the advantages of a gable roof over other types?
A gable roof is simple to design and build, effectively drains precipitation, and evenly distributes loads. Because of this, it often costs less and is more reliable in operation than more complex roofs (for example, hip or broken roofs).
2. What roofing material should be chosen for a cold region?
For cold regions, it is important that the roof retains heat well and withstands heavy snow loads. Optimal choices would be metal tiles or bitumen tiles with adequate insulation. Natural tiles are also a good option, but they are somewhat more expensive and require a sturdier structure.
3. How to calculate the slope angle of the slopes for the roof project?
The angle depends on the climate (wind strength, amount of snow) and the characteristics of the chosen roofing material. Ideally, it should be between 15 and 45 degrees. It is recommended to consult an engineer or use online load calculators.
4. Can the installation of a gable roof be done independently?
Technically — yes, if you have construction experience, tools, and an understanding of the process. However, if you lack skills, it is better to involve professionals: mistakes in design and installation can lead to leaks and unnecessary costs for corrections.
5. Is vapor barrier necessary in the “roofing pie”?
Yes, if you plan to insulate the roof and live under it. The vapor barrier prevents moisture from entering the insulation layer from the rooms, which can cause mold and reduce the thermal insulation properties of the material.
6. What are the most common mistakes when installing a gable roof?
- Incorrect calculation of angles and loads.
- Lack of or poor quality waterproofing and vapor barrier.
- Incorrect spacing of battens, leading to roof deformation.
- Careless sealing of joints and connections (risk of leaks).
7. How often should the roof be repaired or maintained?
It is recommended to inspect the roof twice a year (in spring and autumn). If minor damages are found, it is better to address them immediately, rather than waiting for serious problems to arise.
Conclusion
A gable roof is one of the most rational options for private construction, as it combines simplicity, affordability, and reliability. To ensure that the roofing on your roof serves long and without problems:
- Create a detailed roof project (calculate loads and choose the slope angle).
- Choose quality roofing material, considering the climate and budget.
- Trust the installation to professionals or strictly follow step-by-step instructions when installing it yourself.
- Regularly inspect and maintain the roof to promptly address any deficiencies.
Following these tips will keep the heat in the house, help avoid premature repairs, and increase comfort living in any season.