What is adsorption and absorption: basic concepts of science
Adsorption and absorption are processes that are often confused due to the similarity of their names, but in science, they have fundamentally different meanings.
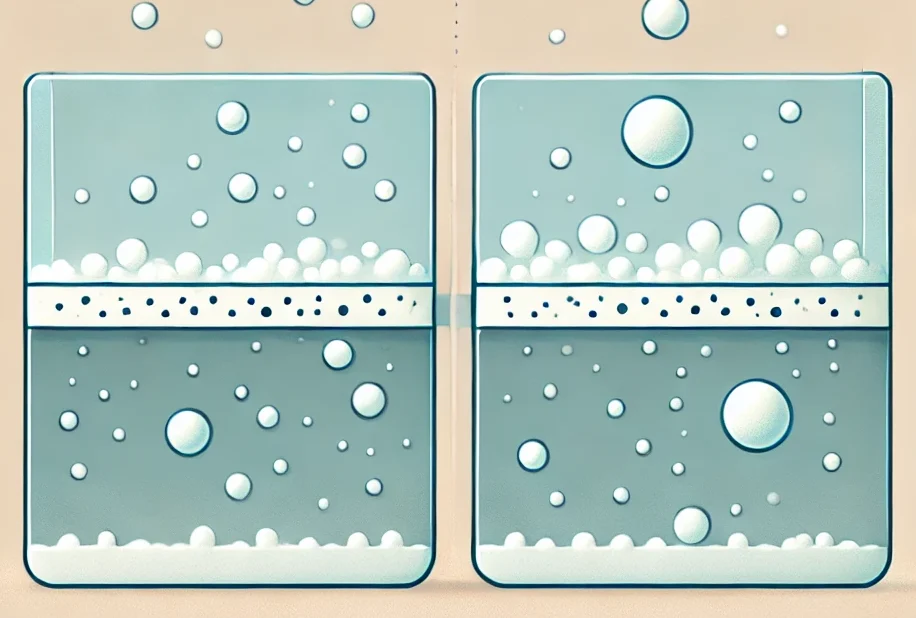
Adsorption is the process by which atoms, molecules, or ions of a substance (adsorbate) settle on the surface of another substance (adsorbent). As a result of this process, an adsorption layer is formed, which can have varying thickness. Adsorption mainly occurs on the surface of solids or liquids.
Absorption, on the other hand, is the process by which one substance (absorbent) completely absorbs another (absorbed substance) and penetrates into its volume. In this case, the absorbed substance is distributed throughout the entire volume of the absorbent. An example of absorption is the uptake of water by plants.
These two processes have their significance in various scientific disciplines, such as chemistry, physics, and biology, and are important for understanding many natural and industrial phenomena.
In-depth exploration: adsorption and absorption in chemistry
In chemistry, adsorption and absorption play an important role in studying reactions and interactions between substances.
Adsorption:
- Physical adsorption: This process occurs based on van der Waals forces. Molecules of the adsorbed substance are attracted to the surface of the adsorbent but do not form chemical bonds. This process is reversible, meaning that the adsorbed material can be easily removed.
- Chemical adsorption: It occurs through the formation of strong chemical bonds between the adsorbed substance and the surface of the adsorbent. This process is usually irreversible.
Absorption:
Absorption can occur in liquid or gaseous states. For example, in chemistry, the process may involve the absorption of gases into liquids (e.g., CO₂ in water) or liquids into solids (e.g., moisture in porous materials).
In both cases, it is important to consider environmental conditions such as temperature, pressure, and concentration, as they can significantly affect the rate and efficiency of these processes.
Key stages of the processes: adsorption vs. absorption
The processes of adsorption and absorption consist of several key stages that are worth examining in more detail.
Key stages of adsorption:
- Approach of molecules: Molecules of the adsorbed substance approach the surface of the adsorbent through diffusion.
- Interaction: Molecules interact with the surface, which may involve physical or chemical bonds.
- Formation of the adsorption layer: Molecules are retained on the surface of the adsorbent, forming an adsorption layer.
Key stages of absorption:
- Contact: The absorbed substance comes into contact with the absorbent.
- Pentration: Molecules penetrate into the volume of the absorbent.
- Distribution: The absorbed substance is evenly distributed throughout the entire volume of the absorbent.
Both processes, although different in nature, can coexist in one environment, leading to complex phenomena in nature and production.
Terminological nuances: how to use terms correctly
The correct use of the terms adsorption and absorption is critically important for accurately describing scientific processes. The terms are often confused, which can lead to misunderstandings in scientific discussions.
When to use the terms:
- Adsorption: Use this term when talking about the process in which substances settle on the surface of another substance. Example: “A gas molecule is adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst.”
- Absorption: Use this term when describing the process of a substance being absorbed into a volume. Example: “Water is absorbed in the porous structure of wood.”
It is also important to note that the terms “adsorbent” and “absorbent” are not interchangeable. An adsorbent is the material on which adsorption occurs, while an absorbent is the material that absorbs another substance.
Interaction of substances: molecules and their behavior in processes
The interaction between molecules is fundamental to understanding both adsorption and absorption. Although both processes may involve similar molecular interactions, their mechanisms differ.
Molecules in adsorption:
- Force interactions: In adsorption, physical (van der Waals) and chemical (covalent) bonds play an important role. For example, gas molecules can adsorb onto the surfaces of solids through weak attractive forces.
- Concentration gradient: The interaction between gases and solid surfaces is often determined by the concentration gradient, where molecules tend to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
Molecules in absorption:
- Diffusion: In absorption, the process of uptake often depends on the diffusion of molecules through the material. This may be related to energy transformations, such as during the absorption of light or heat.
- Solvability: The solubility of the absorbed substance in the absorbent plays an important role. For example, gases like CO₂ dissolve well in water, facilitating their absorption.
Understanding molecular interactions is critically important for studying and optimizing adsorption and absorption processes in various applications.
Scientific methods: how to study adsorption and absorption
Studying adsorption and absorption requires the use of various scientific methods and technologies. This allows researchers to better understand the mechanisms of these processes and find new ways to utilize them.
Methods for studying adsorption:
- Spectroscopy: Used to study the strength and type of bonds formed between adsorbed molecules and the surface of the adsorbent.
- Pore size analysis: Investigates the structure and porosity of adsorbents that affect their adsorption capacity.
- Thermogravimetric analysis: Assesses the change in mass of a sample upon heating or cooling, which can help understand how adsorbed molecules interact with the material.
Methods for studying absorption:
- Solubility measurements: Investigates the solubility of a substance in various environments to determine absorption properties.
- Calorimetry: Measures the heat released or absorbed during absorption, which can indicate energy changes in the process.
- Microscopy: Used to study the structure of relevant materials at the microscopic level to understand how they interact with absorbed substances.
The use of these methods allows scientists not only to study existing processes but also to develop new materials and technologies that may be more effective in implementing adsorption and absorption in various fields.
Practical applications: role in industry and daily life
Adsorption and absorption find wide applications in industry and everyday life. Their importance is hard to overestimate, as these processes are used in various areas, from water purification to the development of new materials.
Applications of adsorption:
- Air purification: Adsorption of gases on activated carbon is used to remove harmful impurities from the air.
- Catalysis: In chemical reactions, the adsorption of reactants on the surfaces of catalysts can increase the reaction rate and its efficiency.
- Pharmaceuticals: Adsorption processes are used to purify and concentrate active components of medications.
Applications of absorption:
- Water treatment: Absorption of pollutants in water, such as heavy metals, using special filters.
- Cooling systems: Absorption cooling systems use combined processes to achieve low temperatures.
- Agricultural chemistry: Absorption processes are used in agronomy for the uptake of water and nutrients by plants.
These examples demonstrate how adsorption and absorption not only impact scientific research but also have direct practical significance for modern life.
Differences in mechanisms: why adsorption and absorption are different
Understanding the difference between adsorption and absorption requires a deeper analysis of the mechanisms underlying these processes.
Mechanisms of adsorption:
- Force interactions: As mentioned, adsorption is based on physical or chemical bonds between molecules. This includes both intermolecular and intramolecular interactions, which can be strong or weak.
- Surface energy: The surface energy of the material plays an important role in adsorption. The higher the surface energy, the greater the likelihood of adsorption.
Mechanisms of absorption:
- Solvability: Absorption requires that the molecules of the absorbed substance be soluble in the absorbent. This means that the chemical nature of both substances is important in the absorption process.
- Pentration: In the absorption process, substances penetrate into the material, which requires energy to overcome intermolecular attractive forces in the absorbent.
These mechanisms show that while adsorption and absorption may appear similar, their physical foundations, energy requirements, and kinetic characteristics are different.
Physical and chemical aspects: how they affect the processes
Physical and chemical aspects play an important role in the processes of adsorption and absorption. Understanding these aspects helps scientists and engineers optimize conditions to achieve maximum results.
Physical aspects:
- Temperature: As temperature increases, adsorption usually decreases, as molecules gain more energy and are less likely to be retained on the surface.
- Pressure: For gases, increasing pressure can enhance the rate of adsorption, as more molecules come into contact with the surface of the adsorbent.
- Porosity: The number and size of pores in the adsorbent can significantly affect the efficiency of adsorption, as greater porosity provides more surface area for adsorption.
Chemical aspects:
- Chemical nature: The interaction between the adsorbent and the adsorbed substances often depends on its chemical nature, which includes polarity, charge, and chemical composition.
- pH of the environment: For absorption, especially in biological systems, pH can significantly affect the solubility and availability of absorbed substances.
These aspects highlight how complex physical and chemical interactions determine the effectiveness of both processes, and why proper management of these variables is critically important for achieving desired results.
Real-life examples: adsorption and absorption in everyday life
The processes of adsorption and absorption are an integral part of our daily lives, and we often encounter their manifestations without even realizing it.
Examples of adsorption:
- Water filtration: Many household water filters use adsorption to remove impurities. For example, activated carbon adsorbs chlorine and organic substances.
- Perfumes: When we use perfumes, their molecules are adsorbed onto the skin and clothing, providing a lasting fragrance.
Examples of absorption:
- Moisture absorption: Hygroscopic materials, such as salt or sugar, absorb moisture from the air, leading to clumping.
- Water in plants: Plants absorb moisture from the soil through their roots, which is necessary for their growth and development.
These examples show how adsorption and absorption affect various aspects of our lives, aiding in resource consumption and supporting health and comfort.
Importance in ecology: the role of these processes in nature
Adsorption and absorption are of significant importance in ecology, as they influence various natural processes and ecosystems.
The impact of adsorption on ecology:
- Soil purification: The adsorption of toxic substances in the soil can help reduce their negative impact on vegetation and animals.
- Water and air: In water and air purification processes, adsorption technologies are used to reduce pollution and maintain environmental cleanliness.
The impact of absorption on ecology:
- Water cycle: The absorption of water by plants is a key element of the hydrological cycle, ensuring the vitality of ecosystems.
- CO₂ absorption: Oceans absorb a large amount of carbon dioxide, contributing to the reduction of the greenhouse effect.
These processes play a critically important role in maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the survival of living organisms on the planet.
Looking to the future: new research and their prospects
Scientific research in the field of adsorption and absorption continues to evolve, opening new opportunities for their use in various areas.
New prospects in adsorption:
- Nanomaterials: Research on nanomaterials for adsorption may lead to the creation of more efficient and faster filters for water and air purification.
- Environmental technologies: New pollution purification technologies that utilize adsorption processes may become the foundation for sustainable development.
New prospects in absorption:
- Biomass materials: Studying natural absorbents to improve agronomic practices may help increase yields and reduce chemical use.
- New energy: Absorption technologies in energy systems can be used for energy storage, contributing to sustainable development.
These research directions demonstrate that adsorption and absorption are not only important for understanding fundamental scientific processes but also open new horizons for addressing pressing issues in the world.